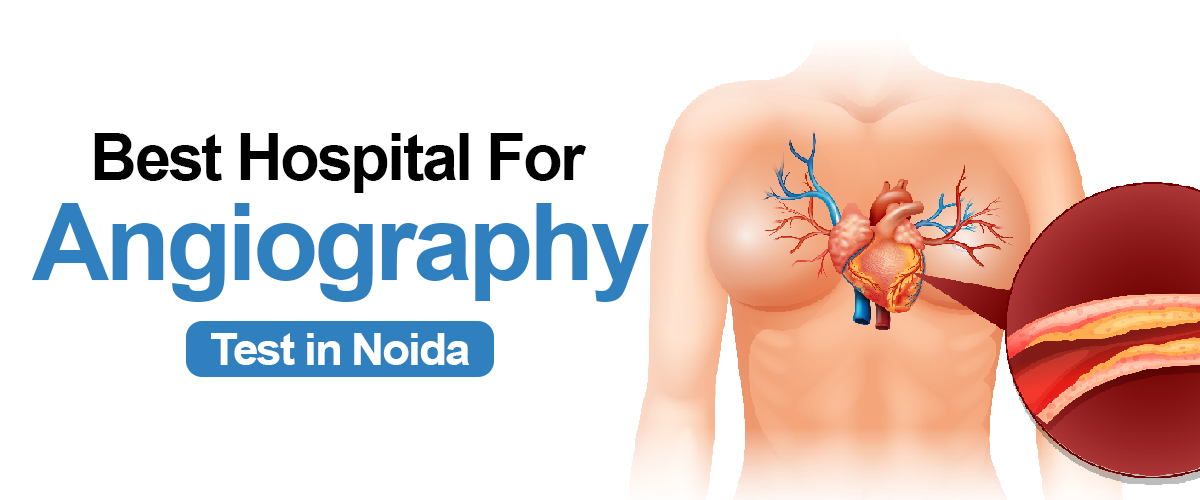
Angiography is a type of X-ray that helps doctors see your blood vessels. Blood vessels do not show clearly on a normal X-ray, so to make them visible, a special dye is injected into your blood. This dye highlights the blood vessels, and the X-ray images created during angiography are called angiograms. It is commonly performed to diagnose and evaluate conditions such as coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and aneurysms. The angiography test time duration can differ based on various factors, such as the complexity of the procedure, the health condition of the patient, and the specific region being examined.
Book Your Appointment One click at +91 9667064100
What is the purpose of using angiography?
Here are some key reasons why angiography is used:
- Identification of causes - Angiography is employed to identify and pinpoint the root causes of various medical conditions.
- Assessment of blood flow - This technique enables the evaluation of blood circulation within the body and helps identify any abnormalities or blockages.
- Diagnosis of cardiovascular issues - Angiography plays a crucial role in diagnosing cardiac and vascular diseases by providing detailed images of blood vessels and identifying potential issues.
- Planning treatment strategies - By gaining a clear understanding of a patient's circulatory system through angiography, medical professionals can plan and execute effective treatment strategies accordingly. When medical procedures or operations are necessary to address issues with blood vessels, angiography is an essential tool in providing guidance. By observing the blood vessels in real-time, medical professionals can accurately navigate through these vessels and administer targeted treatments like stents, materials to block blood flow, or medications. This enhances the precision and efficacy of interventions, including angioplasty or the placement of stents.
- Guidance during surgical procedures - Angiography serves as a valuable tool in guiding surgeons during complex procedures, ensuring precision and accuracy interventions.
- Evaluation of treatment outcomes - This procedure is often used post-treatment to assess the effectiveness of interventions and make any necessary adjustments.
- Prevention and proactive measures - Angiography aids in the early detection and prevention of potential cardiovascular problems, enabling timely interventions and preventive measures.
- Research and advancements - The information gathered from angiography contributes to ongoing research efforts, leading to further advancements in the field of cardiovascular health.
- It can aid in the diagnosis or examination of various issues impacting the blood vessels, such as:
- -Atherosclerosis
- -Peripheral arterial disease
- -Brain Aneurysm
- -Angina
- -Pulmonary embolism
Overall, angiography plays a crucial role in diagnosing, treating, and preventing various cardiovascular conditions, positively impacting patient care and promoting better outcomes.
Angiography Test Process
Here is a step-by-step explanation of the process during angiography:
- Preparations before the procedure: Before the angiography, the patient will typically receive instructions from their healthcare provider on how to get ready. This may involve fasting for a certain period of time before the procedure, stopping certain medications that could interfere with the examination, and obtaining necessary laboratory tests to assess kidney function.
- Placement of the catheter: The patient will be positioned on an X-ray table, and the area where the catheter will be inserted (usually in the groin or arm) will be cleansed and sterilized. Local anesthesia will be administered to numb the area. The interventional radiologist or cardiologist will make a small incision and then place a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into a blood vessel during the angiography test process. This is typically done with the guidance of fluoroscopy, which provides real-time X-ray images.
- Advancement of the catheter: Once the catheter is inside the blood vessel, it will be carefully guided through the arterial system using X-ray imaging as a guide. The catheter is advanced to reach the specific blood vessels or targeted area of interest for examination.
- Injection of contrast: Once the catheter reaches the desired location, a contrast dye is injected through the catheter. This dye can be seen on X-ray imaging and helps to visualize the blood vessels more clearly, allowing the identification of any abnormalities or blockages.
- Image capture: During the angiography test process, the contrast dye circulates through the blood vessels, a series of X-ray images known as angiograms are taken. These images provide detailed information about the structure and function of the blood vessels. The X-ray machine is positioned at different angles to enable visualization of the blood vessels from multiple views.
- Post-procedural care: After the imaging is completed, the catheter is removed and pressure is applied to the insertion site to prevent bleeding. A bandage or compression device may be used to aid in clot formation. The patient will be closely monitored for a short period to ensure there are no complications, such as bleeding or allergic reactions to the contrast dye.
The angiography test time duration can last anywhere from half an hour to two hours. Generally, you will be allowed to return home in a few hours after finishing it.
Potential dangers of Angiography
Although angiography is generally regarded as a safe and efficient process, there are inherent dangers linked to any invasive medical procedure. These risks might differ depending on variables like the patient's overall well-being, the particular type of angiography being conducted, and the proficiency of the medical team involved. Several possible risks of angiography include:.
- Allergic responses: The dye used in angiography may trigger allergic reactions in certain people. Common indications include rashes, itching, nausea, and vomiting. Intense allergic reactions, known as anaphylaxis, can lead to breathing difficulties, accelerated heartbeat, and possibly life-threatening situations. Patients with a history of allergies or previous reactions to contrast dye should communicate this to their healthcare professional before undertaking angiography.
- Contrast-causes kidney damage: There exists a minor possibility of contrast-induced kidney damage, a state in which the kidneys experience temporary dysfunction as a result of the contrast dye. Individuals with pre-existing kidney issues, diabetes, or dehydration face an increased susceptibility. Sufficient fluid intake prior to and following the procedure can reduce the risk of encountering this risk.
- Bleeding or blood clot: Angiography includes placing a catheter into the blood vessels, which carries a slight chance of bleeding or blood clot development at the insertion point. This possibility is greater in individuals with blood-clotting conditions or those consuming anticoagulant drugs. Pressure is exerted on the area following the procedure to avoid bleeding.
- Infection: Although uncommon, there exists a slight possibility of acquiring an infection at the location where the catheter was inserted. The healthcare professionals take necessary precautions to minimize this risk by guaranteeing appropriate sterilization methods are followed.
- Embolism: In certain instances, the handling of blood vessels during angiography can displace a blood clot or other waste, which can move to different regions of the body and result in blockages. This has the potential to lead to severe complexities, like stroke or heart attack. Healthcare experts must vigilantly oversee the process and employ essential measures to prevent embolisms.
- Exposure to radiation: Angiography involves X-rays to view blood vessels. Although the amount of radiation used is typically regarded as safe, repeated exposure over an extended period can increase the risk of specific adverse consequences, like radiation-induced cancers. Nonetheless, the advantages of the technique generally surpass the potential hazards.
Types of angiography
There exist various types of angiography, each specifically designed to capture visuals of particular blood vessels or organs.
- Coronary Angiography: This kind of angiography concentrates on visualizing the blood vessels of the heart. It is frequently utilized to diagnose and evaluate coronary artery disease, where there might be blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries. Throughout Coronary Angiography, a catheter is threaded through an artery (usually in the groin or wrist) towards the heart. A special dye, recognized as a contrast agent, is then injected into the arteries, which helps in visualizing the blood circulation and any possible irregularities. This process is frequently conducted in a cardiac catheterization lab by a skilled interventional cardiologist.
- Cerebral Angiography: Cerebral angiography is employed to examine the blood vessels within the brain. Its primary purpose is to identify irregularities such as aneurysms, abnormal connections between arteries and veins, or blockages within the cerebral arteries. The process entails inserting a thin tube called a catheter into an artery (usually located in the groin area) and skillfully navigating it towards the desired blood vessels in the brain. A special dye is then injected to generate visual representations of the blood vessels through X-ray images. Cerebral angiography is commonly carried out by an interventional neuroradiologist or an interventional neurologist.
- Peripheral Angiography: Peripheral angiography concentrates on the visualization of blood vessels beyond the heart and brain, primarily in the extremities (such as the lower limbs and upper limbs). It aids in the diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease, which refers to the narrowing or blockage of arteries in the legs or arms. The procedure closely resembles coronary and cerebral angiography, wherein a catheter is guided through an artery towards the desired region. To obtain images of the blood vessels, contrast dye is then administered. Peripheral angiography can be conducted by an interventional radiologist, vascular surgeon, or interventional cardiologist.
- Pulmonary Angiography: Pulmonary vascular imaging entails the inspection of blood vessels within the lungs. It is frequently employed for the identification of ailments such as pulmonary thromboembolism (blood clot within the respiratory organs/ lungs) or pulmonary hypertensive disorder ( high blood pressure in the lungs ). Throughout the procedure, a thin tube is inserted into a blood vessel (usually in the groin) and guided towards the pulmonary arteries. A special dye is then administered to visualize the blood vessels while X-ray pictures are captured. Pulmonary vascular imaging is commonly conducted by a specialist in interventional radiology or a specialist in interventional pulmonology.
- Renal Angiography: Renal vascular imaging is specifically focused on examining the blood vessels of the kidneys. It can aid in identifying conditions such as renal artery stenosis ( narrowing ) or assess the blood supply to the kidneys. The process involves placing a thin tube called a catheter into an artery (usually in the groin area) and guiding it towards the renal arteries. A special type of dye is then injected to enhance the visibility of the blood vessels in X-ray images. Renal vascular imaging is commonly conducted by a specialist in interventional radiology or interventional nephrology.
Methods of Angiogram
There are three distinct approaches or methods for conducting angiography tests to detect blockages in blood vessels-.
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA)
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
CTA is less invasive as compared to traditional angiography. It utilizes advanced scanning technology to generate precise images of blood vessels in different areas of the body. To perform this procedure, a special dye is introduced into a vein via an IV line, and several CT scans are conducted while the dye flows through the bloodstream. The Computed Tomography angiography test time duration typically spans between 15 and 45 minutes.
Preparations before angiography
Below are the essential steps to take before undergoing angiography:
- Medical assessment: Prior to undergoing angiography, it is crucial to undergo a thorough medical evaluation. This includes conducting a comprehensive analysis of one's medical history and conducting a physical examination. It is vital to notify the healthcare professional about any hypersensitivities, past surgical procedures, ongoing medications (including anticoagulants), and any prevailing medical ailments, such as diabetes, Kidney issues, or cardiovascular disorders.
- Fasting: Typically, patients are required to fast for a specified period before angiography. This fasting phase guarantees that there is no food in the stomach, which reduces the chance of complications during the procedure. The duration of fasting may differ depending on the particular guidelines given by the healthcare team.
- Medications: The medical professional may advise patients to temporarily stop taking specific medications before angiography. Medications like anticoagulants (e.g., aspirin, warfarin) or anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., ibuprofen) could heighten the chance of bleeding during or after the procedure. It is essential to follow the medical professional's guidance regarding medication control before angiography.
- Blood tests: Prior to angiography, blood tests may be conducted to evaluate different factors, such as total blood count, kidney function, blood clotting capacity, and liver function. These tests assist in determining the patient's overall well-being and contribute to the effective handling of any pre-existing medical conditions that could affect the procedure.
- Considerations for allergies: Some contrast agents used during angiography contain iodine, which can lead to allergic reactions in certain people. Patients who are aware of their allergy to iodine or contrast agents should inform their healthcare provider prior to undergoing the procedure. In these situations, alternative diagnostic approaches may be considered or additional medication could be given beforehand to prevent an allergic reaction.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding : It is crucial to notify the healthcare staff if the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, as certain medical imaging methods used in angiography might potentially endanger the fetus or infant. Under such circumstances, particular precautions might need to be taken to reduce the risk of any potential damage.
Precautions needs to be taken after Angiography Test
After undergoing angiography, it is important to follow certain steps and take necessary precautions to guarantee the best possible recovery and reduce potential risks. Here is what you need to do after undergoing angiography:-
- Rest and Recovery: After the process, it is common to experience fatigue or weakness. It is crucial to take a break for a few hours or as recommended by your healthcare professional. Take it lightly for the rest of the day and avoid engaging in any strenuous activities.
- Watch for complications: Although it is uncommon to encounter complications during angiography, it is important to be mindful of the potential indications of problems. If you experience any worrying symptoms, reach out to your healthcare professional without delay.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration is essential after angiography. Consuming ample amounts of liquids, particularly water, can aid in eliminating the contrast dye used during the procedure and safeguard against dehydration. Nevertheless, avoid consuming excessive amounts of fluids after angiography test. It may strain your kidneys.
- Medication: Your healthcare professional will give you detailed guidance concerning any prescribed medicinal treatments. This may include antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants, which are commonly given to prevent blood clots. It is essential to follow these instructions carefully and take the medication as prescribed.
- Wound care: If your process involves a tube insertion, you may have a minor cut or piercing spot that requires appropriate care. Maintain cleanliness and dryness of the region, following any guidance given by your medical professional. If there are stitches or adhesive strips in place, they will usually be taken out during a follow-up visit.
- Physical exercise: While it is important to rest initially at the beginning, after angiography test, gradually reintroducing physical activity can have positive effects. Your medical professional will provide recommendations on when it is safe to resume regular activities, such as exercise. It is crucial to follow these guidelines, as engaging in demanding activities too early after the angiography procedure could result in complications.
Angiography Test Cost in India
The price of the angiography examination in Noida, India, may differ based on different elements. The kind of angiography, the healthcare establishment or hospital where the test is taking place, and your insurance policy can all impact the price of the examination. Typically, the expense for angiography in Noida can fluctuate between INR 6,999 and INR 15,000. Nevertheless, the cost might increase in case supplementary procedures, like angioplasty or stenting, become necessary.
Simple non-invasive angiography procedures such as CT angiography may range from ₹8,000 to ₹15,000. Conversely, complex procedures like coronary angiography might cost between ₹20,000 to ₹1,50,000, depending on the chosen medical facility. But the angiography test cost in India can vary anywhere from ₹8,000 to ₹1,50,000 or higher, depending on the type and complexity of the procedure.
CT Angiography Test Near Me
CT angiography is a type of medical examination that merges a CT scan with the infusion of a distinct coloring agent to produce visuals of blood vessels and tissues in a part of your body. The coloring agent is administered through an intravenous (IV) tube initiated in your forearm or hand. CT angiography is an essential diagnostic procedure that physicians may utilize to examine an individual's blood vessels. A CT angiography involves a doctor taking numerous X-rays of a person's body. In comparison to coronary angiography, CT angiography incorporates the utilization of multiple X-rays to assist the physician in generating a more detailed image of an individual's blood vessels. It also allows the physician to visualize the blood vessel structure of the patient in two or three dimensions. CT angiography is less invasive than coronary angiography and they pose fewer risks. Now, you will be pleased to learn that Felix Hospital offers the most economical price for CT angiography. The minimum CT angiography test near me can cost ₹ 10500.
Why Felix can be the best Hospital for angiography test in Noida?
We have a group of experienced cardiologists, radiologists, and technicians who excel in conducting angiography tests. We possess state-of-the-art equipment and modern facilities essential for performing the procedure in a safe and efficient manner. In the event of any complications during the angiography procedure, our medical facility is fully equipped to effectively manage emergencies. We have prompt availability to emergency revival tools, specialized medical staff, as well as intensive treatment wards, guaranteeing the well-being of patients at all moments. Searching for a CT angiography test near me will help in locating Felix Hospital. At Felix Hospital, we are committed to providing our patients with transparent and competitive pricing for the procedure compared to the angiography test cost in india.
Book Your Appointment on One click at +91 9667064100